Exploring the Gut-Brain Connection in Anxiety Treatment
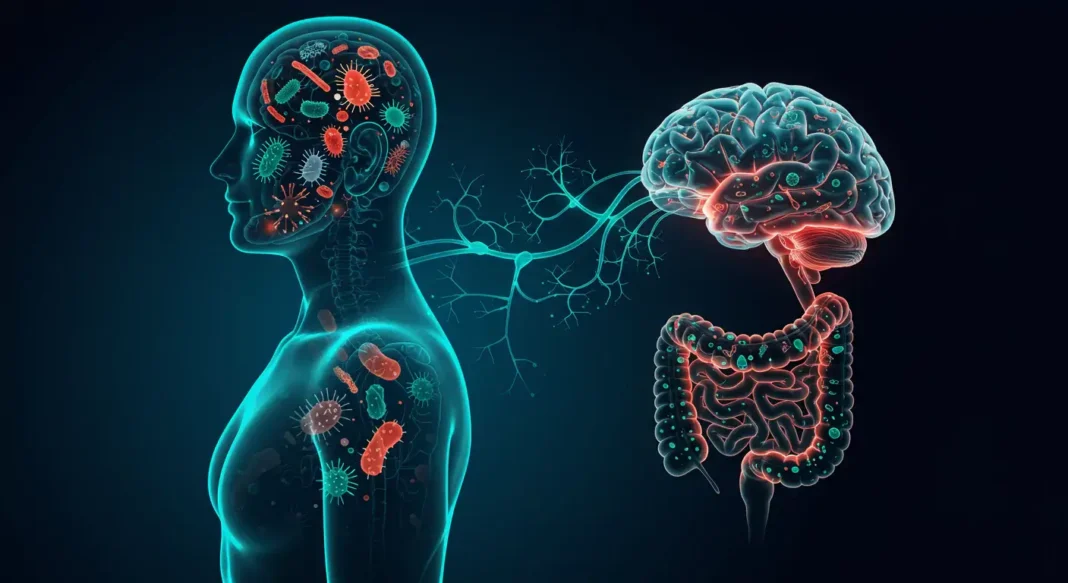
Scientists have discovered that the human gut contains an extensive network of neurons referred to as the “second brain” or enteric nervous system. This complex system communicates directly with the central nervous system through a sophisticated pathway called the gut-brain axis. The communication occurs through neurotransmitters, hormones, and immune system signals that travel between these two critical bodily systems.
Microbiome’s Role in Mental Health
Emerging research reveals that gut bacteria play a significant role in mental health regulation. The microbiome – a collection of trillions of microorganisms living in the digestive tract – can influence mood, stress responses, and anxiety levels. Specific bacterial strains have been linked to neurotransmitter production, including serotonin, which is crucial for emotional regulation.
Key Microbiome Interactions
- Produce neurotransmitters that impact mood
- Regulate inflammation responses
- Modulate stress hormone production
- Influence neural pathways connected to emotional processing
Neurochemical Connections
The gut-brain axis facilitates complex biochemical interactions that directly impact mental health. Approximately 90% of serotonin, a neurotransmitter critical for mood stabilization, is produced in the digestive system. This profound connection explains why digestive health can significantly influence emotional well-being.
Inflammation and Anxiety
Chronic inflammation in the gut can trigger neurological changes that contribute to anxiety symptoms. Inflammatory markers can cross the blood-brain barrier, potentially disrupting neural communication and exacerbating stress responses. Understanding this mechanism opens new avenues for targeted anxiety treatment strategies.
Treatment Approaches
Innovative therapeutic interventions now focus on holistic approaches that address both gut health and mental wellness. Integrative treatments might include:
- Probiotic supplementation
- Personalized dietary modifications
- Stress management techniques
- Targeted microbiome restoration
Dietary Interventions
Nutritional strategies can play a crucial role in managing anxiety through gut-brain axis optimization. Foods rich in prebiotics and probiotics help cultivate a healthy microbiome, potentially reducing anxiety symptoms. Complex carbohydrates, fermented foods, and omega-3 fatty acids have shown promising results in supporting mental health.
Personalized Medicine Potential
Advanced diagnostic techniques now allow healthcare professionals to analyze an individual’s unique microbiome composition. This personalized approach enables more targeted interventions that address specific neurochemical imbalances contributing to anxiety.
Emerging Research Directions
Cutting-edge studies continue exploring the intricate connections between gut health and mental wellness. Researchers are investigating how precise microbiome modulation could offer alternative or complementary treatments for anxiety disorders.
While traditional anxiety treatments remain valuable, the growing understanding of the gut-brain connection provides hope for more comprehensive and personalized mental health interventions. Individuals experiencing anxiety can now consider holistic approaches that encompass both psychological and physiological aspects of their well-being.
Neurological Pathways Linking Digestive Health and Mental Wellness
Modern research demonstrates that the gut microbiome acts as a critical messenger, transmitting signals directly to the brain through multiple neurological pathways. These pathways include the vagus nerve, a superhighway of information that connects the digestive tract to the central nervous system. When the gut microbiome experiences disruption, it can trigger significant changes in brain chemistry and emotional regulation.
Microbiome’s Impact on Emotional Responses
Specific bacterial strains within the gut microbiome produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). These chemical messengers play a fundamental role in mood regulation and anxiety management. Research indicates that approximately 90% of serotonin is actually produced in the digestive system, highlighting the profound connection between gut health and mental wellness.
Key Neurological Communication Mechanisms
- Vagus nerve signaling
- Neurotransmitter production
- Inflammatory response modulation
- Hormonal communication pathways
Inflammation represents another critical link between gut health and mental states. Chronic gut inflammation can trigger systemic inflammatory responses that directly impact brain function. Proinflammatory cytokines released during digestive distress can cross the blood-brain barrier, potentially contributing to anxiety and mood disorders.
Dietary Interventions for Neurological Balance
Nutritional strategies can significantly influence the gut-brain axis. Consuming probiotic-rich foods and maintaining a diverse microbiome helps support neurological health. Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and kimchi introduce beneficial bacterial strains that promote balanced neurotransmitter production.
Nutritional Recommendations
- Consume diverse, fiber-rich foods
- Include probiotic supplements
- Reduce processed sugar intake
- Incorporate omega-3 fatty acids
Stress management techniques also play a crucial role in maintaining gut-brain harmony. Chronic stress can disrupt microbiome balance, leading to increased anxiety and potential mental health challenges. Practices like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity can help modulate stress responses and support digestive system health.
Emerging Treatment Approaches
Cutting-edge research explores targeted interventions that directly address gut-brain communication. Psychobiotics—specialized probiotic strains designed to improve mental health—represent a promising frontier in anxiety treatment. These innovative supplements aim to restore microbiome balance and support neurological function through precise bacterial interactions.
Advanced diagnostic techniques now allow healthcare professionals to assess gut microbiome composition and its potential impact on mental wellness. Personalized treatment plans can be developed by analyzing an individual’s unique microbial landscape, enabling more targeted and effective anxiety management strategies.
Potential Therapeutic Interventions
- Personalized probiotic supplementation
- Microbiome mapping
- Targeted nutritional protocols
- Stress reduction techniques
Understanding the intricate neurological pathways connecting digestive health and mental wellness opens exciting possibilities for comprehensive treatment approaches. By recognizing the gut’s role as more than just a digestive organ, medical professionals can develop holistic strategies that address both physical and psychological well-being.
Microbiome Influences on Emotional Regulation and Stress Response
Your gut is more than just a digestive system – it’s a complex network that plays a crucial role in your emotional well-being. Recent scientific research has uncovered fascinating connections between the microbiome and how your body manages stress and regulates emotions.
The human microbiome consists of trillions of microorganisms living within our digestive system, creating a sophisticated communication network with our brain. These microscopic inhabitants produce neurotransmitters and chemical signals that directly influence mood, anxiety levels, and stress responses.
Neurochemical Pathways of Microbial Communication
Specific bacterial strains in your gut have the remarkable ability to produce key neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). These chemicals are fundamental in regulating emotional states and managing psychological stress. When your microbiome is balanced, it can help stabilize mood and reduce anxiety symptoms.
Stress Response Mechanisms
- Bacterial populations modulate cortisol production
- Influence hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis functioning
- Regulate inflammatory responses linked to emotional dysregulation
The vagus nerve serves as a critical communication highway between your gut and brain. This neural pathway allows microbes to send signals that directly impact neurological processes, potentially altering mood, cognitive function, and stress tolerance.
Inflammatory Connections
Chronic inflammation is increasingly recognized as a significant factor in anxiety and mood disorders. Certain beneficial bacteria help reduce systemic inflammation, creating a protective environment for mental health. Probiotic strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium have demonstrated potential in mitigating inflammatory markers associated with psychological distress.
Practical Strategies for Microbiome Support
Maintaining a diverse and healthy microbiome requires a holistic approach. Dietary choices play a pivotal role in nurturing beneficial bacterial populations that support emotional regulation.
- Consume fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and kimchi
- Include prebiotic-rich vegetables such as garlic, onions, and asparagus
- Minimize processed foods and excessive sugar intake
- Consider targeted probiotic supplementation
Emerging Research Perspectives
Cutting-edge studies are exploring personalized microbiome interventions as potential therapeutic approaches for anxiety management. By understanding individual microbial compositions, researchers hope to develop targeted treatments that address emotional dysregulation at its biochemical roots.
Lifestyle Factors Impacting Microbial Health
Beyond diet, multiple lifestyle elements significantly influence your microbiome’s ability to support emotional balance. Regular exercise, adequate sleep, stress management techniques, and minimizing antibiotic usage can help maintain a robust microbial ecosystem.
Chronic stress can disrupt microbiome diversity, creating a negative feedback loop that exacerbates anxiety symptoms. By implementing holistic wellness strategies, individuals can potentially interrupt this cycle and promote better emotional resilience.
Personalized Wellness Approach
No single intervention works identically for everyone. Individual genetic makeup, environmental factors, and unique microbiome compositions mean that personalized approaches are essential. Consulting healthcare professionals who understand the intricate gut-brain connection can provide tailored guidance for optimizing mental and microbial health.
Understanding the profound relationship between your microbiome and emotional regulation represents a groundbreaking frontier in mental health research. By recognizing the powerful role these microscopic organisms play, individuals can take proactive steps toward improved psychological well-being.
Holistic Approaches to Managing Anxiety Through Gut Health Strategies
The gut-brain axis represents a complex communication network where your digestive system directly influences neurological functioning. Millions of neurons lining the intestinal tract communicate with your brain through biochemical signals, creating a dynamic interaction that impacts emotional regulation and stress response.
Microbiome’s Role in Emotional Wellness
Your gut microbiome—a diverse ecosystem of microorganisms—plays a crucial role in mental health. Beneficial bacteria produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, which significantly influences mood and emotional stability. Approximately 90% of serotonin is actually generated in the digestive system, highlighting the profound connection between gut health and anxiety management.
Strategies for Microbiome Optimization
- Consume fermented foods rich in probiotics
- Include diverse fiber sources in your diet
- Minimize processed food consumption
- Practice stress reduction techniques
Nutritional Interventions for Anxiety Reduction
Dietary choices can dramatically impact anxiety levels by supporting neural pathways and reducing inflammatory responses. Specific nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, and zinc have demonstrated significant potential in modulating neurological function and promoting emotional balance.
Recommended Anxiety-Reducing Nutrients
- Omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish, chia seeds, walnuts)
- Magnesium-rich foods
- Probiotic supplements
- Zinc-containing proteins
Lifestyle Modifications for Gut-Brain Harmony
Beyond nutrition, holistic approaches encompass comprehensive lifestyle adjustments. Regular physical activity, quality sleep, and mindfulness practices can positively influence both gut microbiome composition and neural functioning. Exercise, in particular, stimulates the production of beneficial gut bacteria and reduces stress hormones.
Stress Management Techniques
- Daily meditation practices
- Consistent sleep schedule
- Regular moderate exercise
- Deep breathing exercises
Potential Therapeutic Interventions
Emerging research suggests targeted probiotic strains can potentially alleviate anxiety symptoms. Specific bacterial cultures like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium have shown promising results in clinical studies, demonstrating their capacity to modulate neurotransmitter production and reduce stress responses.
Supplementation Considerations
While promising, individuals should consult healthcare professionals before implementing comprehensive supplementation strategies. Personalized approaches considering individual health histories and specific physiological requirements remain essential.
Environmental and Psychological Factors
Environmental stressors and psychological patterns significantly impact gut health. Chronic stress can alter microbiome composition, potentially triggering inflammatory responses that exacerbate anxiety symptoms. Developing resilience through holistic practices becomes crucial in maintaining optimal gut-brain equilibrium.
Understanding and nurturing the gut-brain connection offers a transformative approach to anxiety management. By integrating nutritional interventions, lifestyle modifications, and targeted strategies, individuals can develop comprehensive wellness frameworks that support both mental and digestive health.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Gut-Brain Axis Interventions for Anxiety Disorders
Emerging scientific studies demonstrate that the gut microbiome plays a critical role in neurotransmitter production and emotional regulation. Specific bacterial strains can generate essential neurochemicals like serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which significantly impact mood and anxiety levels.
Microbiome Composition and Anxiety Mechanisms
Researchers have discovered that individuals with anxiety disorders often exhibit distinct microbiome profiles compared to healthy individuals. These differences suggest that gut bacteria composition can directly influence neurological functioning and emotional processing.
- Reduced microbial diversity correlates with increased anxiety symptoms
- Specific probiotic strains demonstrate potential in modulating stress responses
- Inflammatory markers in the gut can trigger neuroinflammatory processes
Neurochemical Pathways and Inflammatory Responses
The vagus nerve serves as a critical communication highway between the gut and brain, transmitting signals that can dramatically affect mental health. When gut bacteria produce inflammatory compounds, they can potentially disrupt neural signaling and contribute to anxiety manifestations.
Cutting-edge research indicates that probiotic interventions might help rebalance these complex neurochemical pathways. Specific bacterial strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium have shown promising results in reducing anxiety-related behaviors through direct neural modulation.
Potential Treatment Interventions
Clinical investigations have explored various approaches to leverage the gut-brain connection for anxiety management. Targeted probiotic supplementation, dietary modifications, and microbiome restoration techniques emerge as potential therapeutic strategies.
Nutritional interventions focusing on prebiotic and probiotic-rich foods can help cultivate a balanced microbiome. Complex carbohydrates, fermented foods, and specific dietary patterns demonstrate potential in supporting mental health through gut microbiota optimization.
Neuroplasticity and Microbial Influence
Groundbreaking studies reveal that gut microbiota can influence neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to form and reorganize synaptic connections. This suggests that microbiome-targeted interventions might offer long-term neurological benefits for individuals struggling with anxiety disorders.
Advanced neuroimaging techniques have provided visual evidence of how gut bacteria interact with brain regions responsible for emotional processing. These findings underscore the profound interconnectedness between digestive health and mental well-being.
Future Research Directions
While current evidence is promising, researchers emphasize the need for more comprehensive, longitudinal studies to fully understand the gut-brain axis mechanisms. Personalized medicine approaches that consider individual microbiome profiles could revolutionize anxiety treatment paradigms.
Integrative treatment models combining traditional psychiatric interventions with microbiome-focused strategies represent an exciting frontier in mental health management. As scientific understanding deepens, patients may soon benefit from more holistic, targeted approaches to managing anxiety.
The emerging field of psychobiotics—live organisms capable of producing mental health benefits—holds significant potential for developing innovative therapeutic interventions. By understanding the intricate relationship between gut bacteria and neural functioning, researchers continue to unlock new possibilities for anxiety treatment.
Conclusion
The emerging science of the gut-brain connection offers a transformative perspective on anxiety treatment, revealing that mental health is deeply intertwined with our digestive ecosystem. By understanding the complex neurological pathways and microbiome influences, individuals can now approach anxiety management with a more holistic and comprehensive strategy.
Integrating gut health strategies is no longer a fringe approach but a scientifically validated method for emotional regulation and stress reduction. Research consistently demonstrates that targeted interventions—such as probiotic supplementation, dietary modifications, and microbiome-supportive practices—can significantly impact anxiety symptoms.
Patients and healthcare professionals now have powerful tools to address mental wellness from a multidimensional perspective. By recognizing the intricate communication between the digestive system and brain, we can develop more personalized and effective treatment protocols that go beyond traditional pharmaceutical interventions.
The future of anxiety treatment lies in this interconnected understanding. Empowering individuals to optimize their gut health through mindful nutrition, stress management, and targeted supplementation can create lasting improvements in mental resilience and emotional well-being.
While more research is needed, the current scientific evidence strongly supports the potential of gut-brain axis interventions. This approach represents a paradigm shift in mental health treatment, offering hope and practical strategies for those struggling with anxiety disorders.
Ultimately, healing is about understanding the body’s complex systems and supporting them holistically. The gut-brain connection provides a promising pathway toward comprehensive mental health management, bridging the gap between physical and psychological wellness.
The information provided on HealthyPa.com is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. The content on this website, including articles, reviews, and product recommendations, should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or before starting any new supplement, diet, or exercise program. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
The statements regarding dietary supplements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Individual results may vary. The testimonials and experiences shared on this website are individual cases and do not guarantee that you will achieve the same results.
If you are pregnant, nursing, taking medication, or have a medical condition, consult your healthcare provider before using any products reviewed or recommended on this site.
HealthyPa.com and its authors, contributors, and affiliated parties assume no responsibility for any consequences relating directly or indirectly to any action or inaction you take based on the information found on this website.
By using this website, you acknowledge and agree to this disclaimer.
HealthyPa.com is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no additional cost to you. This helps us keep our content free and continue providing valuable health information. We only recommend products we genuinely believe in. Learn more in our full Affiliate Disclosure Policy.